I am really glad to share that my blog is listed among Top 50 Microsoft Azure Blogs, Websites & Influencers in 2020. I am honored to be on this huge list next to other top contributors out of Microsoft Azure communities.
Month: December 2020
Azure Heroes: Content Hero & Community Hero Badger
Today I was awarded with 2 Azure Heroes: Content Hero badger & Community Hero Badger.
If you are not aware of what the Azure Heroes program is, let me explain it to you. Azure Heroes is a new recognition program by Microsoft, which recognizes the members of the technical community with digital badgers for meaningful acts of impact. It’s a blockchain-based recognition program where Microsoft collaborated with Enjin, this blockchain technology is being used for issuance and transactions which means that as a recipient of tokenised badger, you take the ownership of a digital collectible in the form of a non-fungible token (NFT).
Content Hero badgers are given out to those who share valuable knowledge at conferences, meetups or other events. The recipients of this rare award have created original content, sample code or learning resources and documented and shared their experiences and lessons to help others to build on Azure.
Community Hero badgers are given out for contributing materially by organising meetups or conferences or by sharing content and being an active member of the community.
Check other badger categories: Azure Heroes
Find All Azure Heroes: https://www.azureheroes.community/map
My Profile: https://www.azureheroes.community/user/11387
Security Recommendations for Azure App Services
In this article, we will cover the security recommendations that you should follow for establishing a secure baseline configuration for Microsoft Azure App Services on your Azure Subscription.
1. Ensure that App Service’s stack settings should be latest
Newer versions may contain security enhancements and additional functionality. Using the latest software version is recommended to take advantage of enhancements and new capabilities. With each software installation, organizations need to determine if a given update meets their requirements and verify the compatibility and support provided for any additional software against the update revision that is selected.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Configuration under Settings section.
2. Go to General Settings and ensure that your stack should be set to latest version. In the below example, our stack is PHP. Hence, we will select latest PHP version i.e. PHP 7.4
Similarly, in case you are using other stacks like .Net, Python, Java etc. then make sure it should set to latest version. Periodically newer versions are released for software either due to security flaws or to include additional functionality. Using the latest version for web apps is recommended to take advantage of security fixes, if any, and/or additional functionalities of the newer version.
2. HTTP version should be latest
Newer versions may contain security enhancements and additional functionality. Using the latest version is recommended to take advantage of enhancements and new capabilities. With each software installation, organizations need to determine if a given update meets their requirements and also verify the compatibility and support provided for any additional software against the update revision that is selected. HTTP 2.0 has additional performance improvements on the head-of-line blocking problem of old HTTP version, header compression, and prioritization of requests. HTTP 2.0 no longer supports HTTP 1.1\’s chunked transfer encoding mechanism, as it provides its own, more efficient, mechanisms for data streaming.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Configuration under Settings section.
2. Go to General Settings and ensure that HTTP version should be set to latest version. In the below example, the latest HTTP version is 2.0.
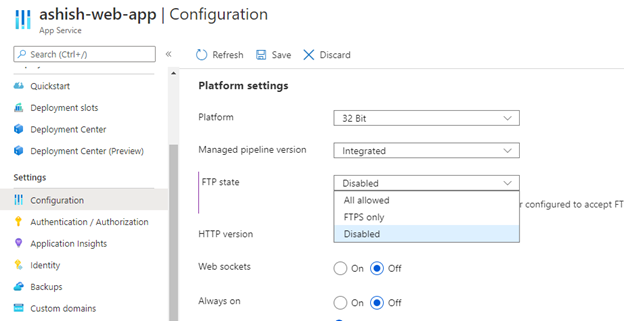
3. Disable FTP deployments
Azure FTP deployment endpoints are public. An attacker listening to traffic on a Wi-Fi network used by a remote employee or a corporate network could see login traffic in cleartext which would then grant them full control of the code base of the app or service. This finding is more severe if User Credentials for deployment are set at the subscription level rather than using the default Application Credentials which are unique per App.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Configuration under Settings section.
2. Go to General Settings and ensure that FTP state should not be All Allowed.
4. Enable Client Certificates mode
Client certificates allow for the app to request a certificate for incoming requests. Only clients that have a valid certificate will be able to reach the app. The TLS mutual authentication technique in enterprise environments ensures the authenticity of clients to the server. If incoming client certificates are enabled, then only an authenticated client who has valid certificates can access the app.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Configuration under Settings section.
2. Go to General Settings and ensure that Client certificate mode should be set to Require.
5. Redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS
Enabling HTTPS-only traffic will redirect all non-secure HTTP request to HTTPS ports. HTTPS uses the SSL/TLS protocol to provide a secure connection, which is both encrypted and authenticated. So it is important to support HTTPS for the security benefits.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on TLS/SSL settings under Settings section.
2. Go to Bindings and set HTTPS Only to ON.
When it is enabled, every incoming HTTP request are redirected to the HTTPS port. It means an extra level of security will be added to the HTTP requests made to the app.
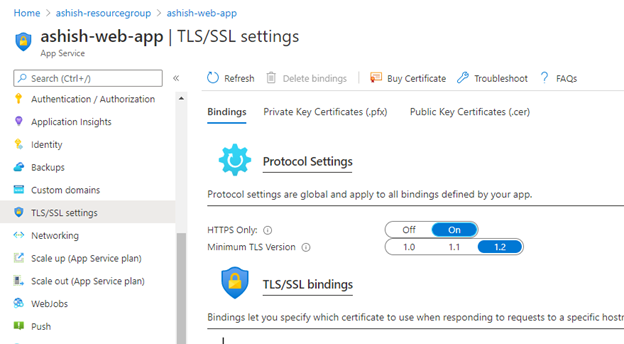
6. Use the latest version of TLS encryption
The TLS(Transport Layer Security) protocol secures transmission of data over the internet using standard encryption technology. Encryption should be set with the latest version of TLS. App service allows TLS 1.2 by default, which is the recommended TLS level by industry standards, such as PCI DSS. App service currently allows the web app to set TLS versions 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2. It is highly recommended to use the latest TLS 1.2 version for web app secure connections.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on TLS/SSL settings under Settings section.
2. Go to Bindings and ensure that TLS Version should be latest version. Here the latest version is 1.2.
7. Enable App Service Authentication
Azure App Service Authentication is a feature that can prevent anonymous HTTP requests from reaching the API app, or authenticate those that have tokens before they reach the API app.
By Enabling App Service Authentication, every incoming HTTP request passes through it before being handled by the application code. It also handles authentication of users with the specified provider(Azure Active Directory, Facebook, Google, Microsoft Account, and Twitter), validation, storing and refreshing of tokens, managing the authenticated sessions, and injecting identity information into request headers.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Authentication / Authorization under Settings section.
2. Set App Service Authentication to ON
If an anonymous request is received from a browser, App Service will redirect to a logon page. To handle the logon process, a choice from a set of identity providers can be made, or a custom authentication mechanism can be implemented.
8. Enable System Assigned Managed Identity
Managed service identity in App Service makes the app more secure by eliminating secrets from the app, such as credentials in the connection strings. When registering with Azure Active Directory in the app service, the app will connect to other Azure services securely without the need of username and passwords.
Steps:
1. Open your App Service and click on Identity under Settings section.
2. Set the Status to ON
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/web-sites-configure#general-settings
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/app-service-authentication-overview
Security Recommendations for Azure SQL Database
In this article, we will cover the security recommendations that you should follow for establishing a secure baseline configuration for Microsoft Azure SQL Services on your Azure Subscription.
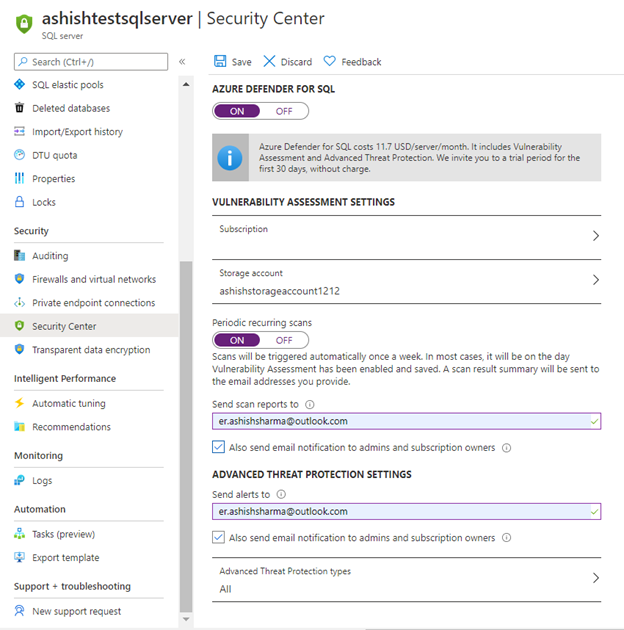
1. Enable auditing on SQL Servers & SQL databases:
Steps:
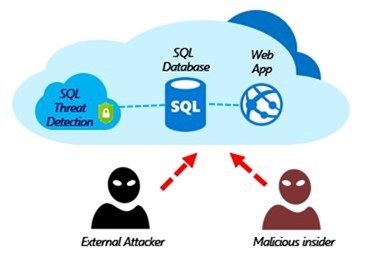
2. Enable threat detection on SQL Servers & SQL databases:
Steps:
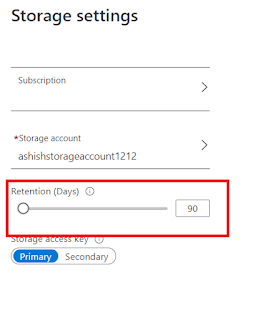
3. Configure Retention policy greater than 90 days.
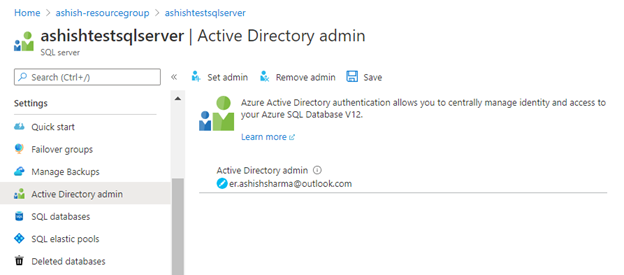
4. Use Azure Active Directory Authentication for authentication with SQL Database
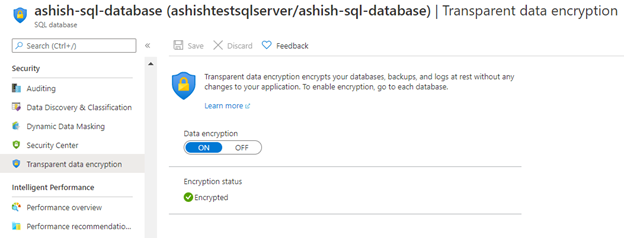
5. Enable Data encryption on SQL database
Steps:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-threat- detection
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-auditing
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/encryption/transparent-data-encryption-with-azure-sql- database
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/sql-database/sql-database-auditing